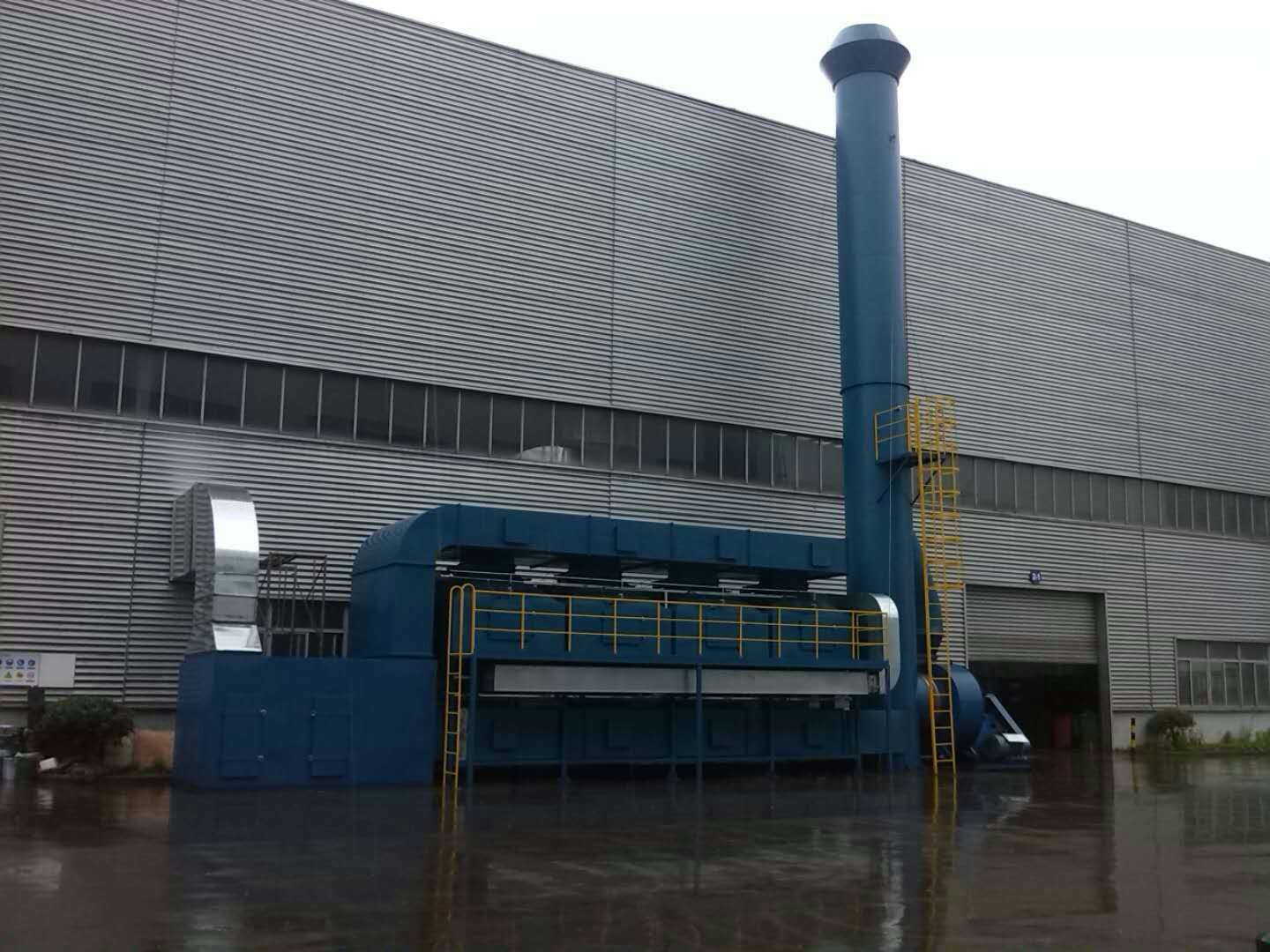
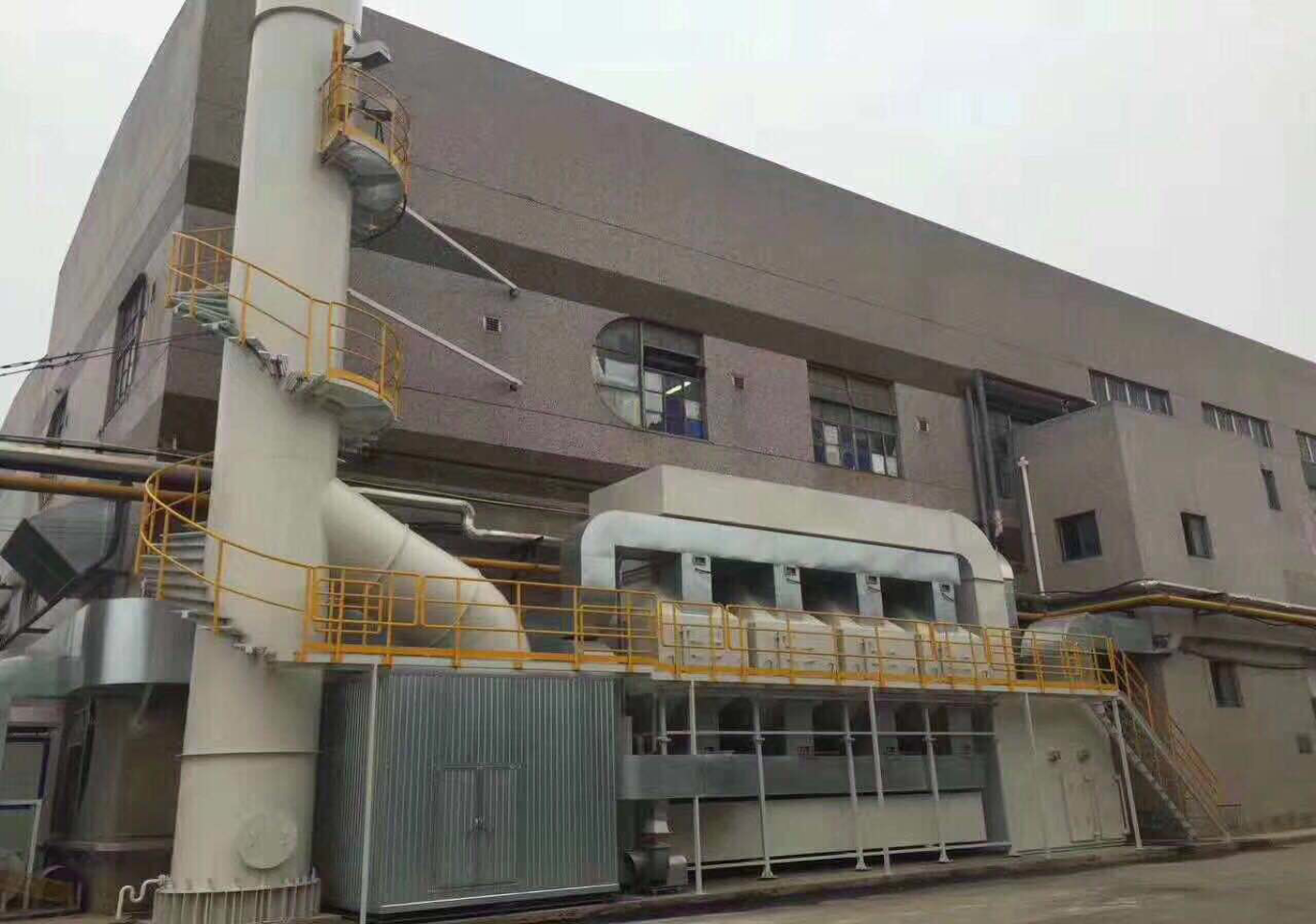
Catalytic combustion process
In the chemical reaction process, the method of using the catalyst to reduce the combustion temperature and accelerate the complete oxidation of toxic and harmful gases is called the catalytic combustion method. Because the carrier of the catalyst is made of porous material, with a large specific surface area and a suitable pore size, when the organic gas heated to 300~450 ℃ passes through the catalytic layer, oxygen and organic gas are adsorbed on the catalyst on the surface layer of the porous material , Increase the chance of contact and collision between oxygen and organic gas, improve the activity, make the organic gas and oxygen produce a violent chemical reaction to generate CO2 and H2O, and generate heat at the same time, so that the organic gas becomes non-toxic and harmless gas.
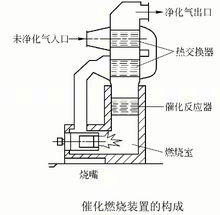
The catalytic combustion device is mainly composed of heat exchangers, combustion chambers, catalytic reactors, heat recovery systems, and exhaust stacks for purifying flue gas, as shown on the right. The purification principle is: before entering the combustion chamber, the unpurified gas is preheated by the heat exchanger and sent to the combustion chamber, and the required reaction temperature is reached in the combustion chamber. The oxidation reaction proceeds in the catalytic reactor. The gas releases part of the heat through the heat exchanger and is discharged into the atmosphere by the chimney.
The following aspects should be considered when designing a catalytic combustion device:
1. Airflow and temperature are evenly distributed. To make the airflow and temperature distribution through the catalyst surface uniform, and to ensure that the flame does not directly contact the catalyst surface, the combustion chamber must have sufficient length and space. The catalytic combustion device should have a good thermal insulation effect. The furnace body is generally lined with refractory material in the outer shell of the steel structure, or a double-layer sandwich wall structure.
2. Easy to clean and replace. The catalyst reactor should generally be designed with a convenient drawer structure to facilitate cleaning and replacement of the catalyst carrier.
3. Auxiliary fuel and combustion support. Catalytic combustion generally uses natural gas as auxiliary fuel, and fuel oil, electric heating, etc. can also be used as auxiliary fuel. Combustion generally uses purified gas. If the purified gas cannot be used as combustion aid, air combustion should be introduced.
4. Higher conversion speed. Since catalytic combustion is an irreversible exothermic reaction, no matter what stage the reaction proceeds to, it should be carried out at the highest possible temperature to obtain a higher conversion rate. However, the operating temperature is often limited by certain conditions, such as the heat-resistant temperature of the catalyst, the acquisition of high-temperature materials, the supply of heat energy, and whether it is accompanied by side reactions. Therefore, the actual production should be properly selected according to the actual situation.
Materials and carriers
A catalyst is a substance that can change the speed of a chemical reaction without changing its chemical properties before and after the reaction. The catalyst is usually composed of a catalytically active material and a catalytic carrier. The catalytically active material is generally a metal or metal oxide. Among them, precious metal catalysts mainly include platinum, palladium and ruthenium, and common metal catalysts mainly include copper, chromium, nickel, vanadium, manganese, iron, cobalt and other metals and oxides. The catalytic carrier is a porous material, and its main function is to make the active material have a large body surface area. The catalytic carrier is divided into metal carrier, ceramic carrier and carbon fiber carrier. Metal carriers are generally in the shape of belts, sheets, pellets, wires, etc. made of nickel or nickel-chromium alloys, and platinum and palladium are plated on these carriers by "electroplating" or "electroless plating" (ie, solution dipping), and It is made into a drawer that is easy to assemble and disassemble. Ceramic-based catalysts generally use silicon-aluminum oxide as the carrier, and its structure has two types: flake and honeycomb. Generally, a thin layer of α-alumina with a thickness of only 0.13mm is coated on the ceramic structure, and the active platinum, palladium and other metal catalysts are deposited or dispersed in the porous aluminum oxide layer in a microcrystalline state, and made easy The drawer for assembly and disassembly. The carbon fiber carrier can be made into linear, felt, net and other shapes, and the catalytically active material is coated on the carrier to make a mold drawer that is convenient for assembly and disassembly.
Performance requirements
The catalyst is the core of the catalytic combustion method. A good catalyst must have the characteristics of high catalytic activity, good thermal stability, high strength and long life.
1. High activity. The activity of the catalyst directly affects the chemical conversion rate of catalytic combustion. The conversion rate is not only related to the activity of the catalytically active material itself, but also directly related to the physical shape of the catalytic carrier. Therefore, while selecting suitable catalytically active materials, it is also necessary to consider the physical shape of the catalytic carrier to ensure that the catalyst has high activity and achieve the purpose of catalytic combustion purification.
2. Good thermal stability. Since the temperature of the exhaust gas changes at any time, if the catalyst cannot adapt to the temperature change within a certain range, the performance of the catalyst will decrease and the purification efficiency will decrease. Therefore, the catalyst must be able to adapt to temperature changes within a certain range.
3. High strength. In the process of catalytic combustion, the catalyst often causes the catalyst to crack and wear due to the effects of high temperature, vibration and airflow. Cracking and wear will reduce the activity of the catalyst, increase the pressure drop of the catalyst bed, and affect the purification effect.
4. Long life. Most of the catalytically active materials are relatively expensive, so when designing, the catalyst should have a catalyst with a longer service life.
Catalytic combustion applications
Catalytic combustion is suitable for the purification of toxic and harmful gases containing combustible gases, steam, etc., but for the toxic and harmful gases containing a large amount of dust particles, mist droplets, etc., it is easy to cause clogging of the catalytic bed, which reduces the catalytic activity and thus reduces the purification efficiency. The catalytic combustion purification method is suitable for almost all industrial production processes that emit hydrocarbons or odorous compounds.